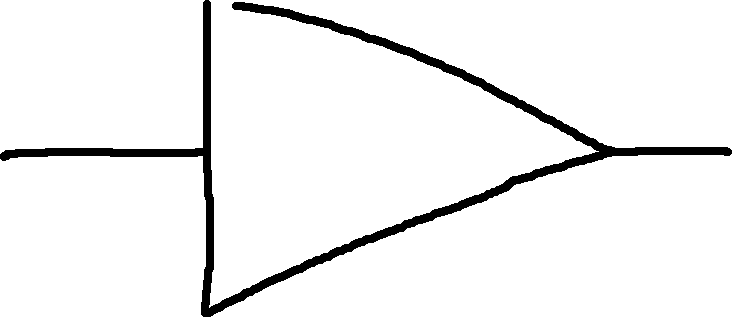

Buffer: Anything you put in, you get out.
| In | Out |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 |
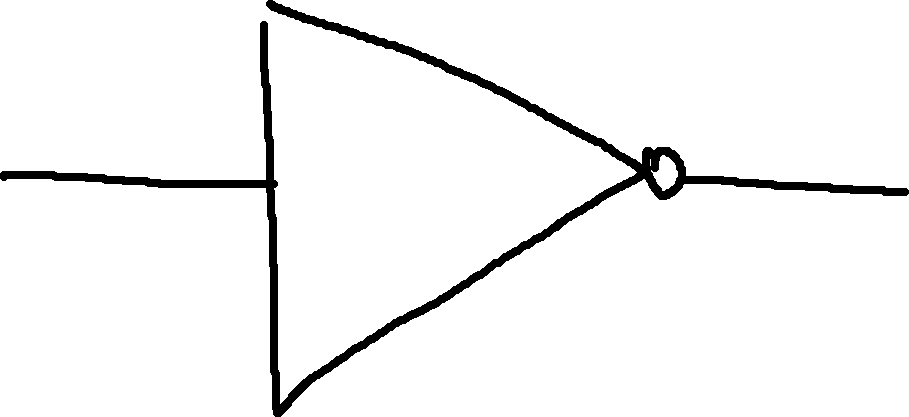
NOT: Flip the signal.
| In | Out |
|---|---|
| 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 |
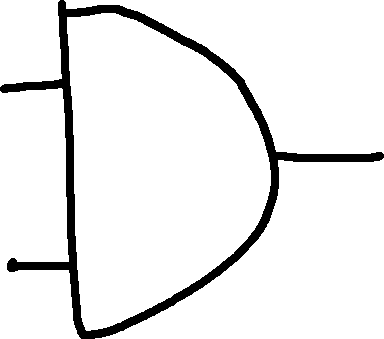
AND: If both are 1, return 1; otherwise return 0.
| A | B | Out |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
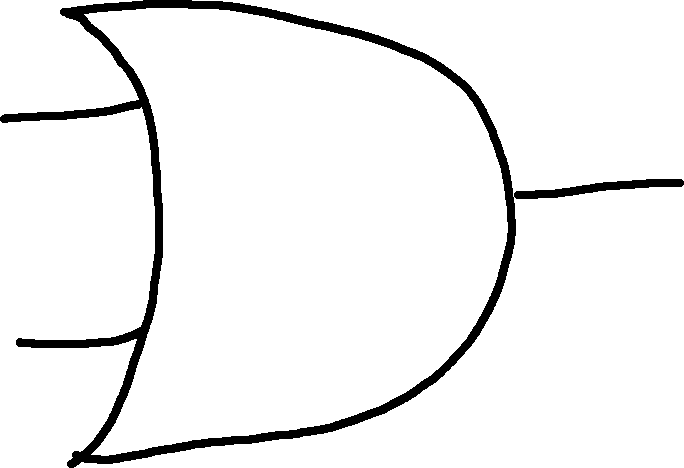
OR: Inclusive OR
| A | B | Out |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
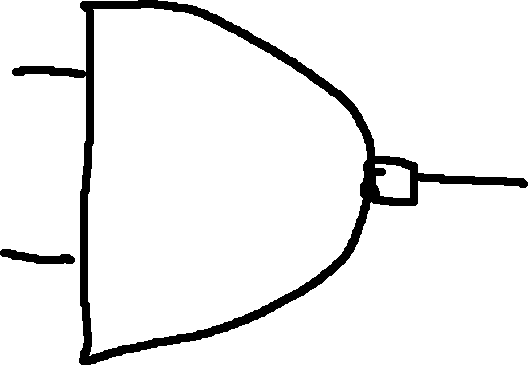
NAND: NOT AND
| A | B | Out |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
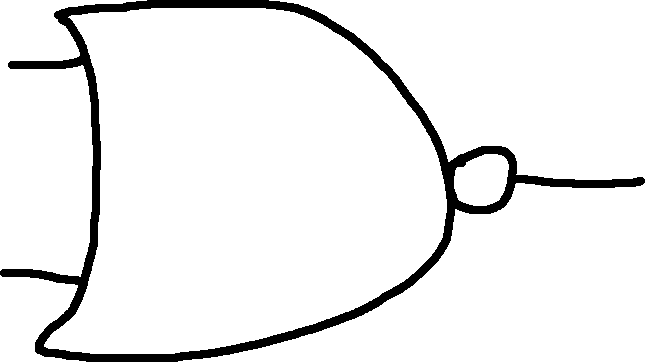
NOR: NOT OR
| A | B | Out |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
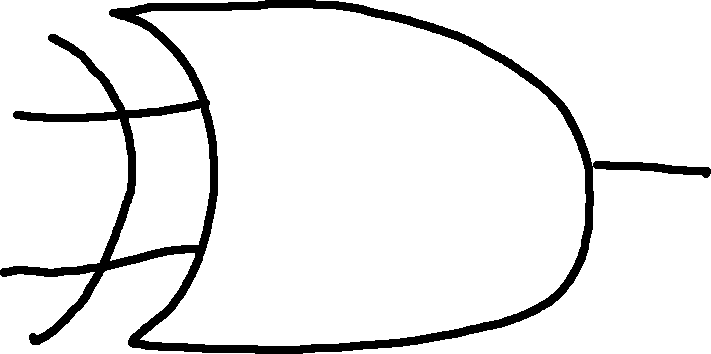
XOR: Exclusive OR
| A | B | Out |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
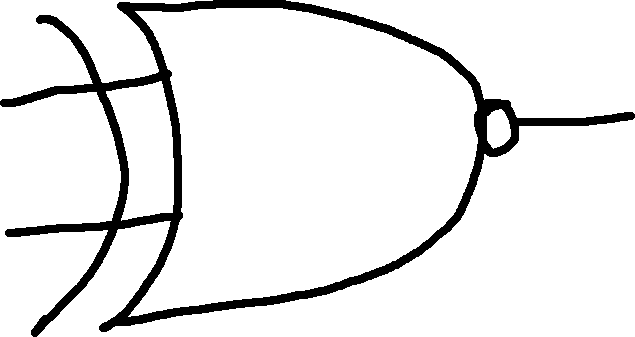
XNOR: Exclusive NOR
| A | B | Out |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
NAND and NOR can create all the basic logic gates.
NOT:
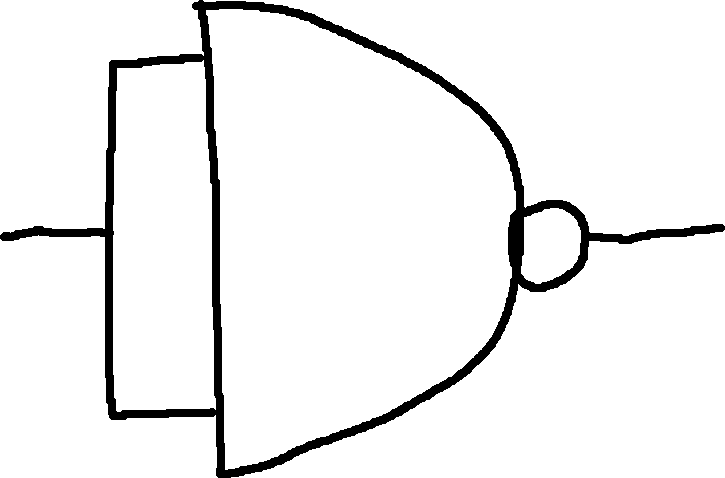
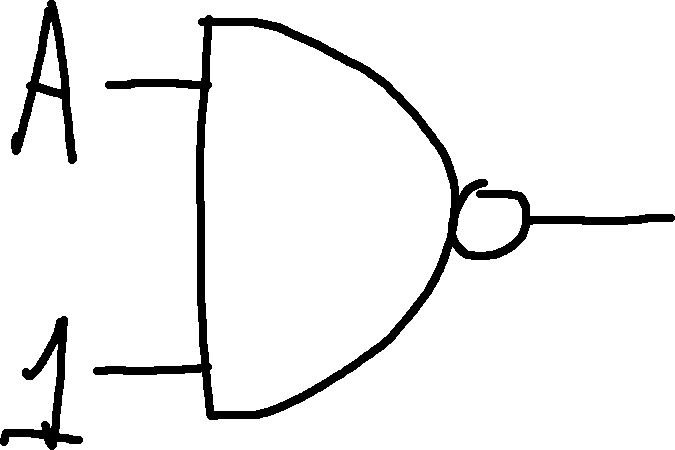
OR:
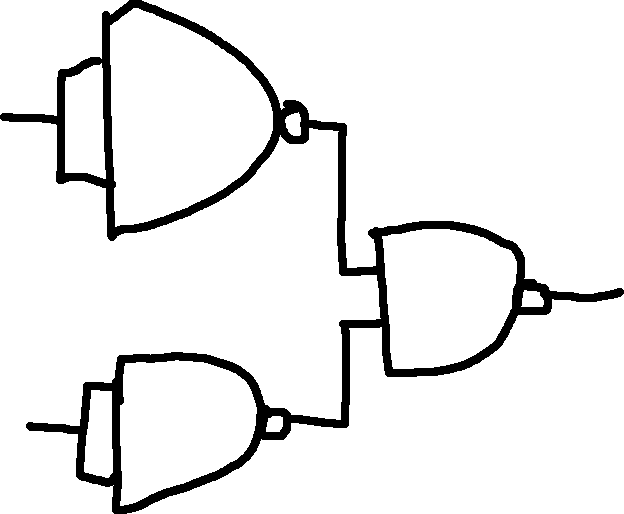
AND:
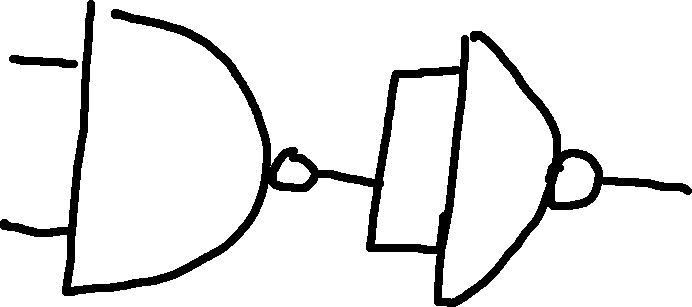
NOT:
AND:
OR:
NAND:
MUX: Functions like a switchboard.
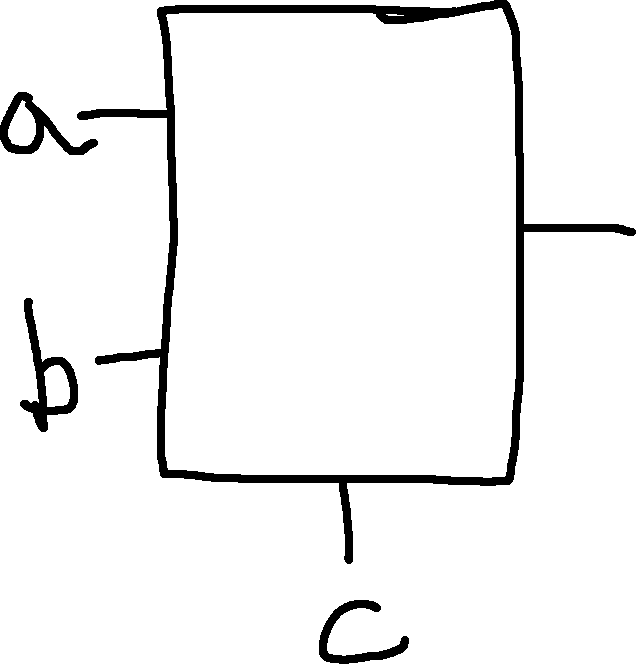
This MUX takes three inputs, a, b, and c.
| c | out |
|---|---|
| 0 | a |
| 1 | b |
c'a+cb
We can make any basic logic gate with a MUX.
Suppose we want to configure a MUX to give this truth table:
| a | b | out |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
We want to split the table into two states first.
| a | b | out |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| a | b | out |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
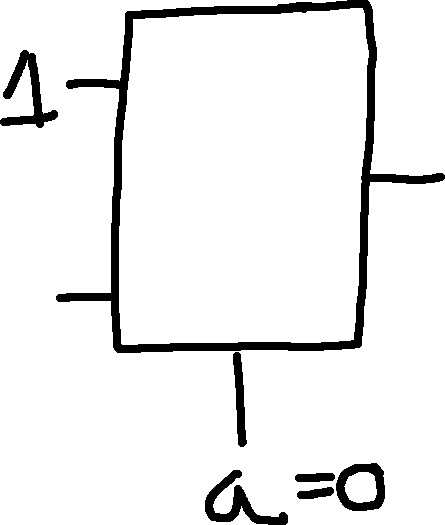
Observation: We can immediately see that when a=0, out is always 1, so we can draw a partial MUX like this:
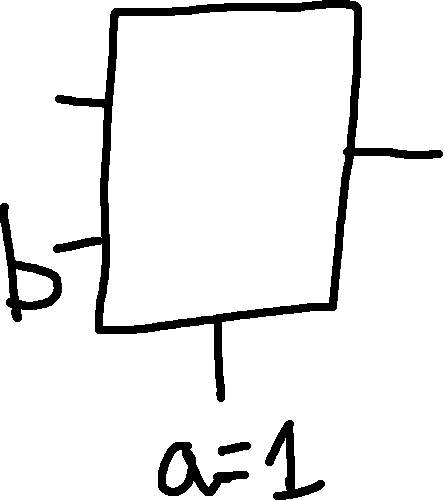
Observation: Looking at the other truth table, we can see that out is always b when a=1, so we can draw a partial MUX like this:
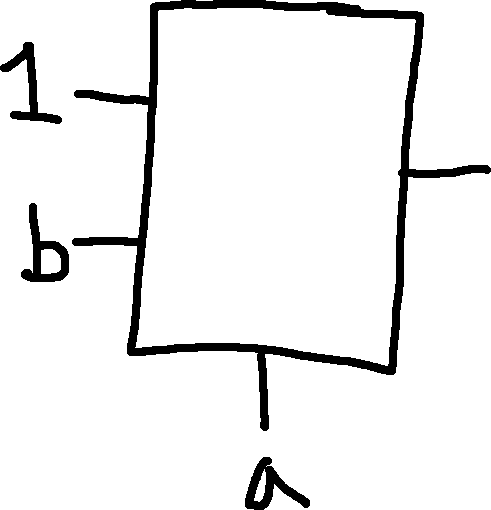
Putting it all together, the final MUX is this:
TODO draw a 4:1 MUX
This MUX takes six inputs, a, b, c, d, x, and y
| x | y | out |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | a |
| 0 | 1 | b |
| 1 | 0 | c |
| 1 | 1 | d |
TODO draw a 8:1 MUX
| x | y | z | out |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | a |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | b |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | c |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | d |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | e |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | f |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | g |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | h |